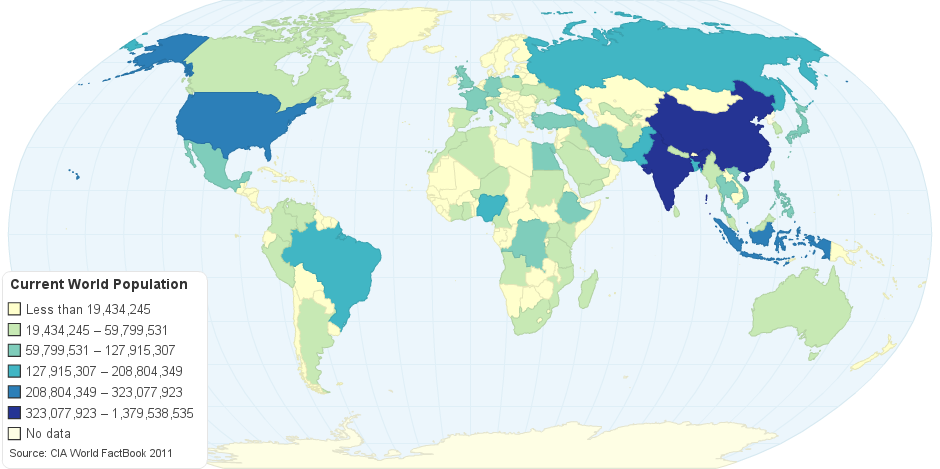
This map shows an estimate from the US Bureau of the Census based on statistics from population censuses, vital statistics registration systems, or sample surveys pertaining to the recent past and on assumptions about future trends.
Current world population: 7,395,740,068 (Jan 2016 est.)
In demographics, the world human population is the total number of humans living on Earth. As of Jan 2016, it was estimated at 7.3 billion. The United Nations estimates it will increase to 11.2 billion in the year 2100.
The world human population has experienced continuous growth since the end of the Great Famine and the Black Death in 1350, when it was near 370 million. The highest growth rates – global population increases above 1.8% per year – occurred briefly during the 1950s, and for longer during the 1960s and 1970s. The global growth rate peaked at 2.2% in 1963, and has declined to 1.1% as of 2012. Total annual births were highest in the late 1980s at about 139 million, and are now expected to remain essentially constant at their 2011 level of 135 million, while deaths number 56 million per year, and are expected to increase to 80 million per year by 2040. World population reached 7 billion on October 31, 2011 according to the United Nations Population Fund and on March 12, 2012 according to the United States Census Bureau.
The 2012 UN projections show a continued increase in population in the near future with a steady decline in population growth rate; the global population is expected to reach between 8.3 and 10.9 billion by 2050. 2003 UN Population Division population projections for the year 2150 range between 3.2 and 24.8 billion. One of many independent mathematical models supports the lower estimate, while a 2014 estimate forecasts between 9.3 and 12.6 billion in 2100, and continued growth thereafter.Some analysts have questioned the sustainability of further world population growth, highlighting the growing pressures on the environment, global food supplies, and energy resources.
10 years ago