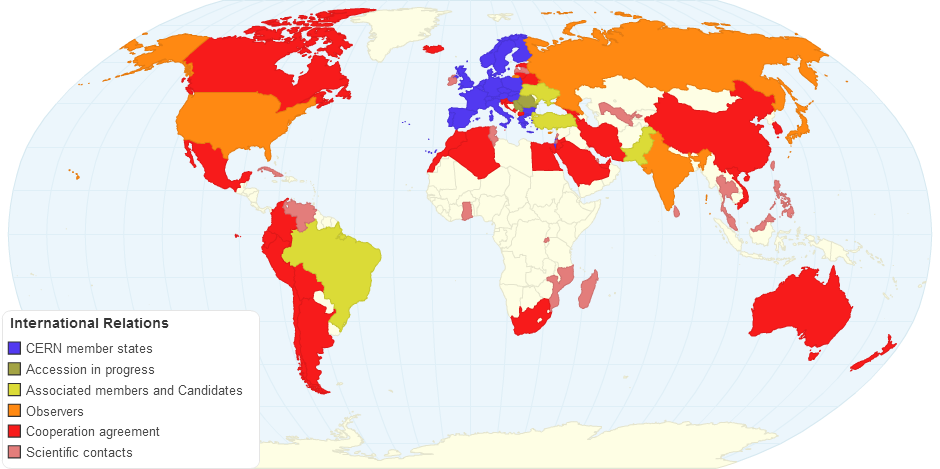
This chart shows the CERN International Relations...
The European Organization for Nuclear Research known as CERN is a European research organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, the organization is based in a northwest suburb of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border and has 21 member states.Israel is the first non-European country granted full membership.
The term CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory, which in 2013 had 2,513 staff members, and hosted some 12,313 fellows, associates, apprentices as well as visiting scientists and engineers representing 608 universities and research facilities.CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research – as a result, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN as a result of international collaborations.CERN is also the birthplace of the World Wide Web. The main site at Meyrin has a large computer facility containing powerful data processing facilities, primarily for experimental-data analysis; because of the need to make these facilities available to researchers elsewhere, it has historically been a major wide area networking hub.
Since its foundation by 12 members in 1954, CERN regularly accepted new members. All new members have remained in the organization continuously since their accession, except Spain and Yugoslavia. Spain first joined CERN in 1961, withdrew in 1969, and rejoined in 1983. Yugoslavia was a founding member of CERN but quit in 1961. Of the 21 members, Israel joined CERN as a full member on 6 January 2014, becoming the first non-European full member.
10 years ago