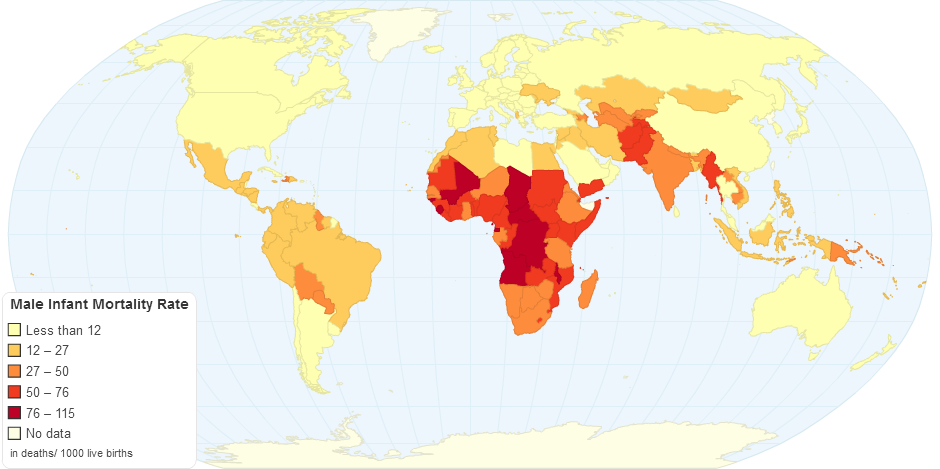
This chart shows Male Infant Mortality Rate by Country.
The infant mortality rate (IMR) is the number of deaths of infants under one year old per 1,000 live births. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country. The infant mortality rate of the world is 49.4 according to the United Nations and 42.09 according to the CIA World Factbook.
The leading causes of infant mortality are birth asphyxia, pneumonia, term birth complications, neonatal infection, diarrhea, malaria, measles and malnutrition. Many factors contribute to infant mortality, such as the mother's level of education, environmental conditions, and political and medical infrastructure. Improving sanitation, access to clean drinking water, immunization against infectious diseases, and other public health measures can help reduce high rates of infant mortality.
In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to premature infants, postmature infants, and full term infants. Before birth, the term fetus is used. In the UK, infant is a term that can be applied to school children aged between four and seven. As a legal terminology, "infancy" continues from birth until age 18.
10 years ago