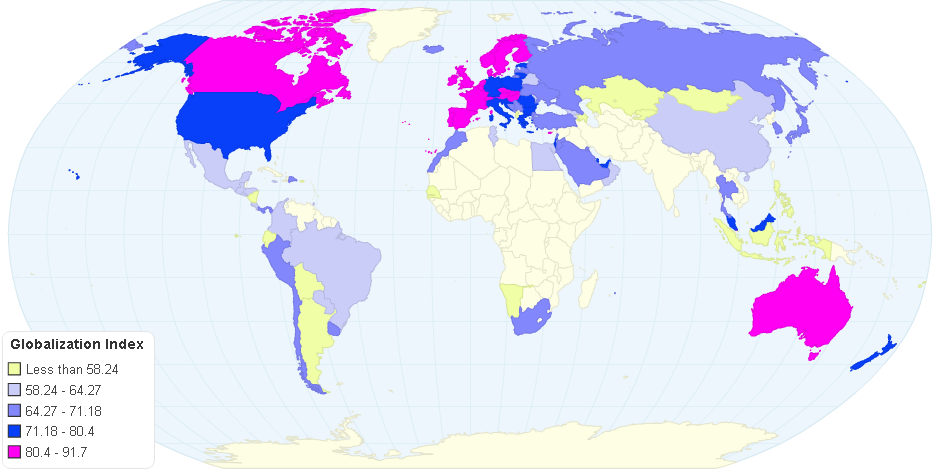
This chart shows Globalization index 2016.
Globalization is the process of international integration arising from the interchange of world views, products, ideas and other aspects of culture.Advances in transportation, such as the steam locomotive, steamship, jet engine, container ships, and in telecommunications infrastructure, including the rise of the telegraph and its modern offspring, the Internet, and mobile phones, have been major factors in globalization, generating further interdependence of economic and cultural activities.
Early modern globalization is distinguished from modern globalization on the basis of expansionism, the method of managing global trade, and the level of information exchange. The period is marked by such trade arrangements as the East India Company, the shift of hegemony to Western Europe, the rise of larger-scale conflicts between powerful nations such as the Thirty Year War, and a rise of new commodities – most particularly slave trade. The Triangular Trade made it possible for Europe to take advantage of resources within the western hemisphere.
globalization approached its modern form as a direct result of the industrial revolution. Industrialization allowed standardized production of household items using economies of scale while rapid population growth created sustained demand for commodities. In the 19th century, steamships reduced the cost of international transport significantly and railroads made inland transport cheaper.
Globalizing processes affect and are affected by business and work organization, economics, socio-cultural resources, and the natural environment. Academic literature commonly subdivides globalization into three major areas:
1. Economic globalization,
2. Cultural globalization and
3. Political globalization.
10 years ago