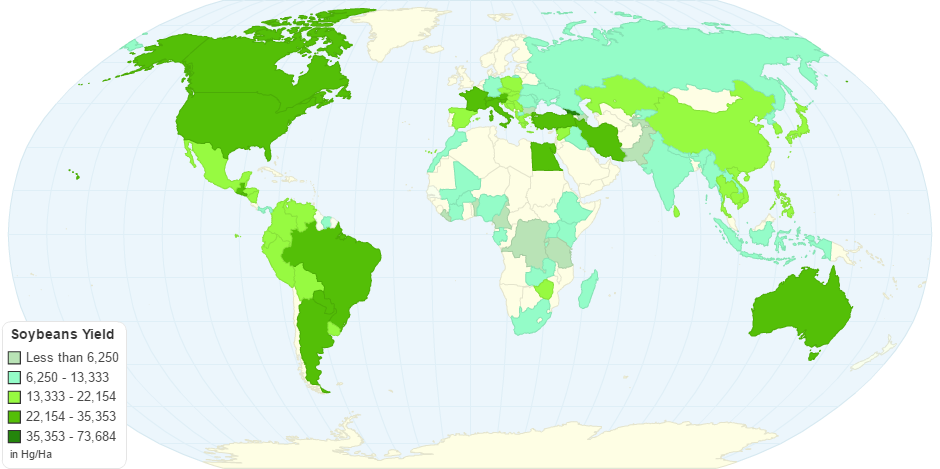
This chart shows Soybeans Yield by Country.
Glycine max, commonly known as soybean in North America or soya bean in British English, is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean which has numerous uses. The plant, classed as an oilseed rather than a pulse by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, produces significantly more protein per acre than most other uses of land.
Fat-free soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. The beans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop.
Soybeans are a globally important crop, providing oil and protein. In the United States, the bulk of the harvest is solvent-extracted with hexane, and the "toasted" defatted soymeal then makes possible the raising of farm animals on a large industrial scale. Soybean products are used in a large variety of processed foods.
Cultivation is successful in climates with hot summers, with optimum growing conditions in mean temperatures of 20 to 30 °C (68 to 86 °F); temperatures of below 20 °C and over 40 °C (68 °F, 104 °F) stunt growth significantly. They can grow in a wide range of soils, with optimum growth in moist alluvial soils with a good organic content. Soybeans, like most legumes, perform nitrogen fixation by establishing a symbiotic relationship with the bacterium Bradyrhizobium japonicum. For best results, though, an inoculum of the correct strain of bacteria should be mixed with the soybean seed before planting.
Global production of soybeans is forecast to be 324 million tonnes in 2016, a 5% increase from the 2014 world total.The United States, Brazil and Argentina are the world's largest soybean producers and represent more than 80% of global soybean production.
10 years ago