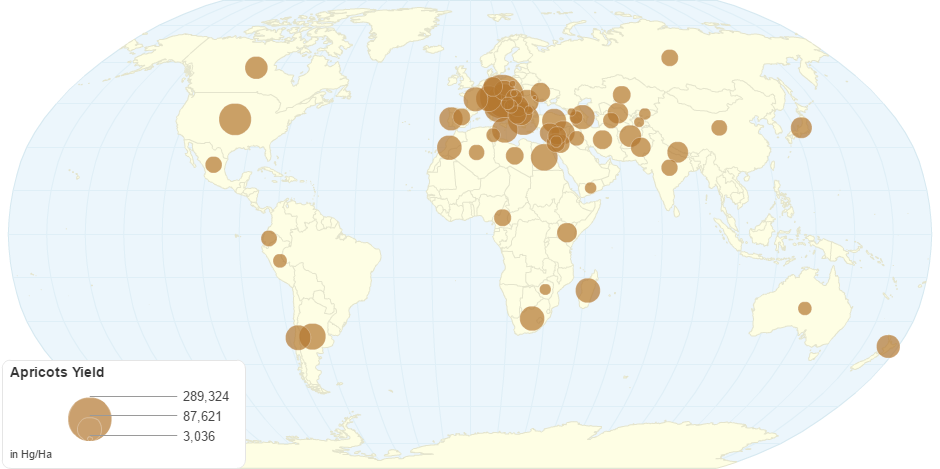
This chart shows Apricots Yield by Country.
An apricot is a fruit or the tree that bears the fruit of several species in the genus Prunus. Usually, an apricot tree is from the species P. armeniaca, but the species P. brigantina, P. mandshurica, P. mume, and P. sibirica are closely related, have similar fruit, and are also called apricots.
The apricot is a small tree, 8–12 m tall, with a trunk up to 40 cm in diameter and a dense, spreading canopy. The leaves are ovate, 5–9 cm long and 4–8 cm wide, with a rounded base, a pointed tip and a finely serrated margin. The flowers are 2–4.5 cm in diameter, with five white to pinkish petals; they are produced singly or in pairs in early spring before the leaves.
The fruit is a drupe similar to a small peach, 1.5–2.5 cm diameter, from yellow to orange, often tinged red on the side most exposed to the sun; its surface can be smooth or velvety with very short hairs . The flesh is usually firm and not very juicy. Its taste can range from sweet to tart. The single seed is enclosed in a hard, stony shell, often called a "stone", with a grainy, smooth texture except for three ridges running down one side.
Apricots are susceptible to various diseases whose relative importance is different in the major production regions as a consequence of their climatic differences. For example, hot weather as experienced in California's Central Valley will often cause pit burn, a condition of soft and brown fruit around the pit.
9 years ago