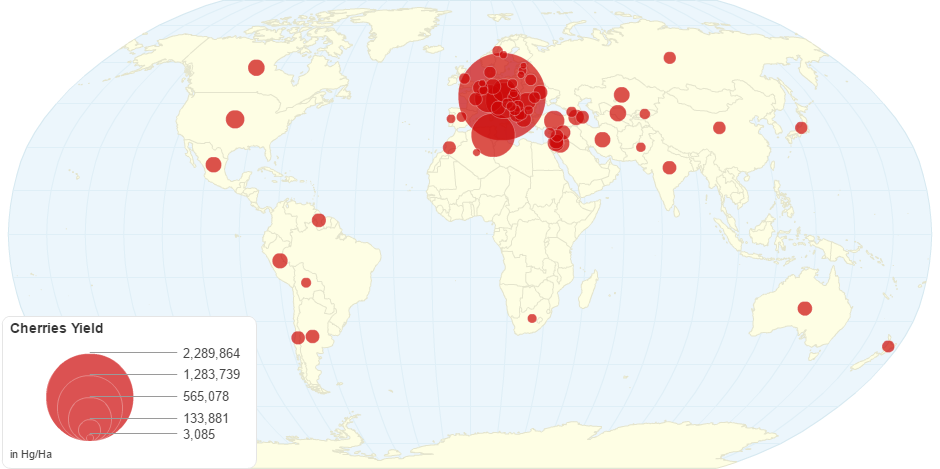
This chart shows Cherries Yield by Country.
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus Prunus, and is a fleshy drupe. The cherry fruits of commerce usually are obtained from a limited number of species such as cultivars of the sweet cherry, Prunus avium. The name 'cherry' also refers to the cherry tree, and is sometimes applied to almonds and visually similar flowering trees in the genus Prunus, as in "ornamental cherry", "cherry blossom", etc.
Wild Cherry may refer to any of the cherry species growing outside of cultivation, although Prunus avium is often referred to specifically by the name "wild cherry" in the British Isles.
The cultivated forms are of the species sweet cherry to which most cherry cultivars belong, and the sour cherry , which is used mainly for cooking. Both species originate in Europe and western Asia; they do not cross-pollinate. Some other species, although having edible fruit, are not grown extensively for consumption, except in northern regions where the two main species will not grow.
Irrigation, spraying, labor, and their propensity to damage from rain and hail make cherries relatively expensive. Nonetheless, demand is high for the fruit. In commercial production, cherries are harvested by using a mechanized 'shaker'. Hand picking is also widely used to harvest the fruit to avoid damage to both fruit and trees.
Common rootstocks include Mazzard, Mahaleb, Colt, and Gisela Series, a dwarfing rootstock that produces trees significantly smaller than others, only 8 to 10 feet tall. Sour cherries require no pollenizer while few sweet varieties are self-fertile.
9 years ago