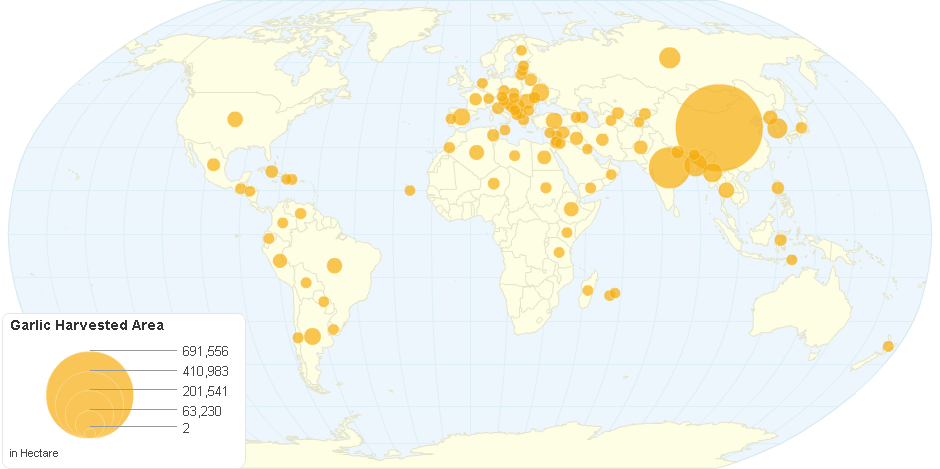
This chart shows Garlic Harvested Area by Country.
Allium sativum, commonly known as garlic, is a species in the onion genus, Allium.Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive,and rakkyo.With a history of over 7,000 years of human consumption and use, garlic is native to central Asia,and has long been a staple in the Mediterranean region, as well as a frequent seasoning in Asia, Africa, and Europe. It was known to Ancient Egyptians, and has been used both as a food flavoring and as a traditional medicine.
Garlic is easy to grow and can be grown year-round in mild climates. While sexual propagation of garlic is possible, nearly all of the garlic in cultivation is propagated asexually, by planting individual cloves in the ground. In colder climates, cloves are planted in the autumn, about six weeks before the soil freezes, and harvested in late spring or early summer. The cloves must be planted deep enough to prevent freeze/thaw, which causes mold or white rot.
Garlic plants can be grown closely together, leaving enough space for the bulbs to mature, and are easily grown in containers of sufficient depth.
Garlic does well in loose, dry, well-drained soils in sunny locations, and is hardy throughout USDA climate zones 4–9. When selecting garlic for planting, it is important to pick large bulbs from which to separate cloves. Large cloves, along with proper spacing in the planting bed, will also improve bulb size.
There are different varieties or subspecies of garlic, most notably hardneck garlic and softneck garlic. The latitude where the garlic is grown affects the choice of type, as garlic can be day-length sensitive. Hardneck garlic is generally grown in cooler climates; softneck garlic is generally grown closer to the equator.Garlic scapes are removed to focus all the garlic's energy into bulb growth. The scapes can be eaten raw or cooked.
9 years ago