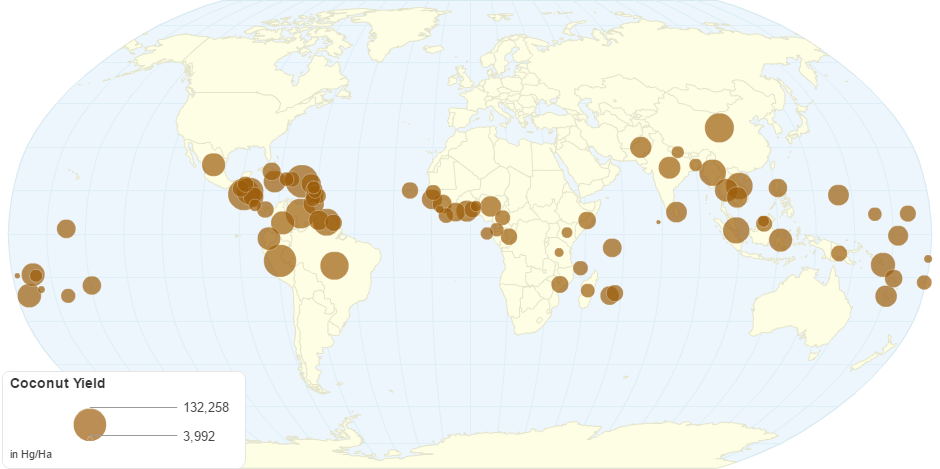
This chart shows Coconut Yield by Country.
The coconut tree is a member of the family Arecaceae and the only species of the genus Cocos.The term coconut can refer to the entire coconut palm or the seed, or the fruit, which, botanically, is a drupe, not a nut. The spelling cocoanut is an archaic form of the word.The term is derived from the 16th-century Portuguese and Spanish word coco meaning "head" or "skull", from the three indentations on the coconut shell that resemble facial features.
Coconuts are known for their great versatility, as evidenced by many traditional uses, ranging from food to cosmetics.They form a regular part of the diets of many people in the tropics and subtropics. Coconuts are distinct from other fruits for their large quantity of "water", and when immature, they are known as tender-nuts or jelly-nuts and may be harvested for their potable coconut water. When mature, they still contain some water and can be used as seednuts or processed to give oil from the kernel, charcoal from the hard shell, and coir from the fibrous husk.
Coconut palms are grown in more than 90 countries of the world, with a total production of 61 million tonnes per year. Most of the world production is in tropical Asia, with Indonesia, the Philippines, and India accounting collectively for 73% of the world total.
The various parts of the coconut have a number of culinary uses. The seed provides oil for frying, cooking, and making margarine. The white, fleshy part of the seed, the coconut meat, is used fresh or dried in cooking, especially in confections and desserts such as macaroons. Desiccated coconut or coconut milk made from it is frequently added to curries and other savory dishes. Coconut flour has also been developed for use in baking, to combat malnutrition.
9 years ago