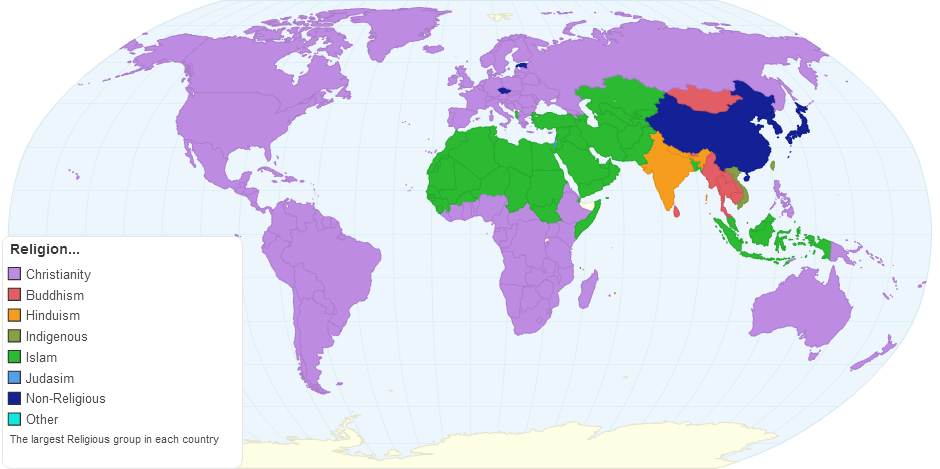
This chart shows the World Religion.
Religion is a cultural system of behaviors and practices, world views, ethics, and social organisation that relate humanity to an order of existence.About 84% of the world's population is affiliated with one of the five largest religions, namely Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism or folk religion.The study of religion encompasses a wide variety of academic disciplines, including comparative religion and social scientific studies.
Theories of religion offer explanations for the origins and workings of religion.With the onset of the modernisation of and the scientific revolution in the western world, some aspects of religion have cumulatively been criticized. Though the religiously unaffliated, including Atheism and Agnosticism, have grown globally, many of the unaffiliated still have various religious beliefs. About 16% of the world's population is religiously unaffiliated.Issues in some way related to religion include "Reason and science", economics, health, and morality.
Religious traditions fall into super-groups in comparative religion, arranged by historical origin and mutual influence. Abrahamic religions originate West Asia, Indian religions in the Indian subcontinent and East Asian religions in East Asia. Another group with supra-regional influence are Afro-American religion, which have their origins in Central and West Africa.
Middle Eastern religions:
1.Abrahamic religions are the largest group, and these consist mainly of Christianity, Islam, Judaism and the Bahá'í Faith. They are named for the patriarch Abraham, and are unified by the practice of monotheism. Today, around 3.4 billion people are followers of Abrahamic religions and are spread widely around the world apart from the regions around East and Southeast Asia. Several Abrahamic organizations are vigorous proselytizers.
2.Iranian religions (not listed below due to overlaps), partly of Indo-European origins, includes Zoroastrianism, Yazdânism, Ætsæg Din, Ahl-e Haqq and historical traditions of Gnosticism . It has significant overlaps with Abrahamic traditions, e.g. in Sufism and in recent movements such as Bábism and the Bahá'í Faith.
3.Indian religions, originated in Greater India and partly of Indo-European origins, they tend to share a number of key concepts, such as dharma, karma, reincarnation among others. They are of the most influence across the Indian subcontinent, East Asia, Southeast Asia, as well as isolated parts of Russia. The main Indian religions are Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism and Sikhism.
4.East Asian religions consist of several East Asian religions which make use of the concept of Tao or Dō . They include many Chinese folk religions, Taoism and Confucianism, as well as Korean and Japanese religion influenced by Chinese thought.
5.African religions: The religions of the tribal peoples of Sub-Saharan Africa, but excluding ancient Egyptian religion, which is considered to belong to the ancient Middle East;African diasporic religions practiced in the Americas, imported as a result of the Atlantic slave trade of the 16th to 18th centuries, building on traditional religions of Central and West Africa.
6.Indigenous ethnic religions, found on every continent, now marginalized by the major organized faiths in many parts of the world or persisting as undercurrents of major religions. Includes traditional African religions, Asian shamanism, Native American religions, Austronesian and Australian Aboriginal traditions, Chinese folk religions, and postwar Shinto. Under more traditional listings, this has been referred to as "paganism" along with historical polytheism.
7.New religious movement is the term applied to any religious faith which has emerged since the 19th century, often syncretizing, re-interpreting or reviving aspects of older traditions such as Ayyavazhi, Mormonism, Ahmadiyya, Pentecostalism, polytheistic reconstructionism, and so forth.
10 years ago