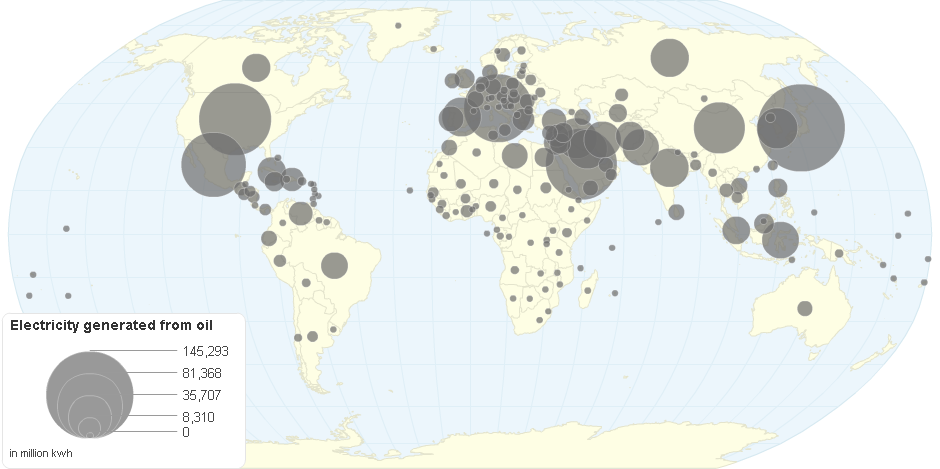
This chart shows The Oil Power by Country.
An oil is any neutral, nonpolar chemical substance that is a viscous liquid at ambient temperatures and is both hydrophobic and lipophilic . Oils have a high carbon and hydrogen content and are usually flammable and slippery.
The general definition of oil includes classes of chemical compounds that may be otherwise unrelated in structure, properties, and uses. Oils may be animal, vegetable, or petrochemical in origin, and may be volatile or non-volatile.They are used for food, fuel, lubrication, and the manufacture of paints, plastics, and other materials. Specially prepared oils are used in some religious ceremonies as purifying agents.
Oil is the largest source of energy in the United States, providing close to 40 percent of all of the nation's entire power needs. Though most oil is used for transportation or home heating purposes, a small percentage is still used as a fuel for electricity generating plants.
Three technologies are used to convert oil into electricity:
1. Conventional steam - Oil is burned to heat water to create steam to generate electricity.
2. Combustion turbine - Oil is burned under pressure to produce hot exhaust gases which spin a turbine to generate electricity.
3. Combined-cycle technology - Oil is first combusted in a combustion turbine, using the heated exhaust gases to generate electricity. After these exhaust gases are recovered, they heat water in a boiler, creating steam to drive a second turbine.
10 years ago