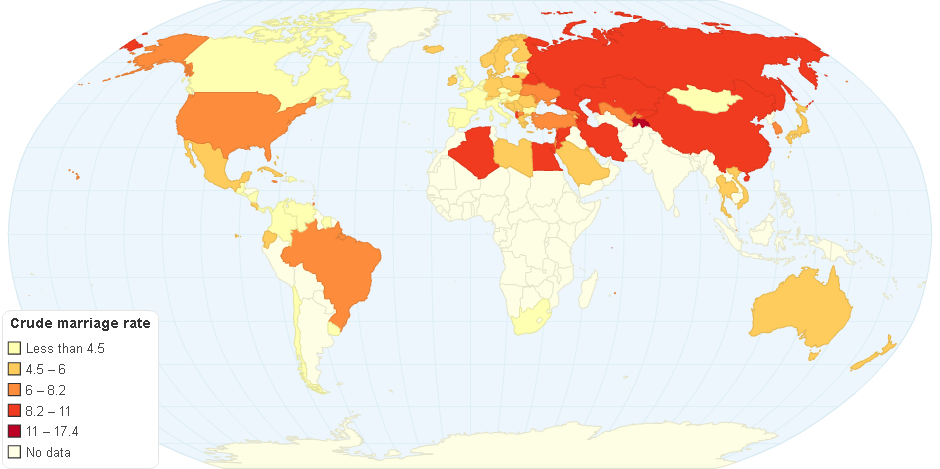
This chart shows Divorce Statistics by Country.
Divorce is the termination of a marriage or marital union, the canceling and/or reorganizing of the legal duties and responsibilities of marriage, thus dissolving the bonds of matrimony between a married couple under the rule of law of the particular country and/or state.
Divorce laws vary considerably around the world, but in most countries divorce requires the sanction of a court or other authority in a legal process, which may involve issues of alimony , child custody, child visitation / access, parenting time, child support, distribution of property, and division of debt. In most countries, monogamy is required by law, so divorce allows each former partner to marry another person; where polygyny is legal but polyandry is not, divorce allows the woman to marry a new husband.
Divorce should not be confused with annulment, which declares the marriage null and void; with legal separation or de jure separation or with de facto separation . Reasons for divorce vary, from sexual incompatibility or lack of independence for one or both spouses to a personality clash. Divorce rates increase during times of hardship, war, and major events.
Divorce rates increased after World War II because people were quick to marry each other before they went to war. When soldiers returned, they found out they don't have much in common with their spouses, so they divorced. According to a study published in the American Law and Economics Review, women have filed slightly more than two-thirds of divorce cases in the United States.
This trend is mirrored in the UK where a recent study into web search behavior found that 70% of divorce inquiries were from women. These findings also correlate with the Office for National Statistics publication "Divorces in England and Wales 2012 which reported that divorce petitions from women outnumber those from men by 2 to 1.
9 years ago