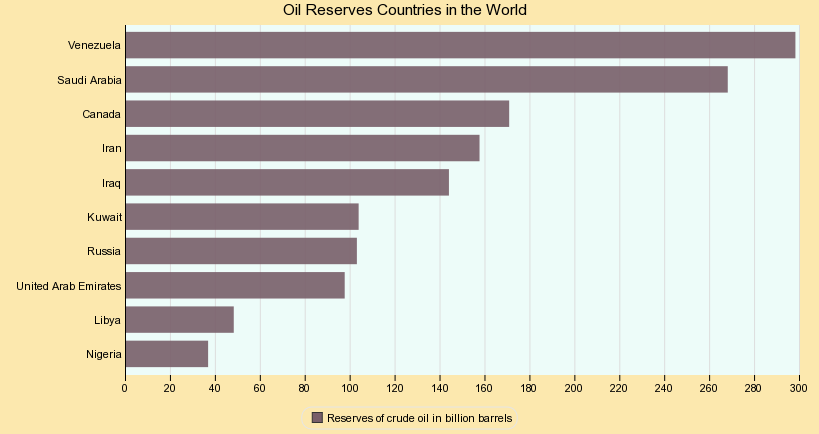
This chart shows Oil Reserves Countries in the World.
An oil is any neutral, nonpolar chemical substance that is a viscous liquid at ambient temperatures and is both hydrophobic and lipophilic . Oils have a high carbon and hydrogen content and are usually flammable and slippery.
Oil reserves are the amount of technically and economically recoverable oil. Reserves may be for a well, for a reservoir, for a field, for a nation, or for the world. Different classifications of reserves are related to their degree of certainty.
The total estimated amount of oil in an oil reservoir, including both producible and non-producible oil, is called oil in place. However, because of reservoir characteristics and limitations in petroleum extraction technologies, only a fraction of this oil can be brought to the surface, and it is only this producible fraction that is considered to be reserves. The ratio of reserves to the total amount of oil in a particular reservoir is called the recovery factor.
The geology of the subsurface cannot be examined directly, indirect techniques must be used to estimate the size and recoverability of the resource. While new technologies have increased the accuracy of these techniques, significant uncertainties still remain. In general, most early estimates of the reserves of an oil field are conservative and tend to grow with time. This phenomenon is called reserves growth.
Many oil-producing nations do not reveal their reservoir engineering field data and instead provide unaudited claims for their oil reserves. The numbers disclosed by some national governments are suspected of being manipulated for political reasons.
9 years ago