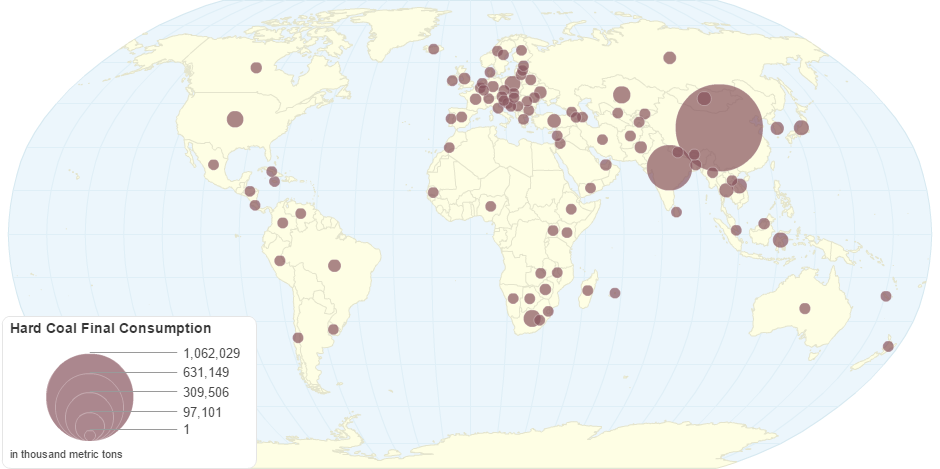
This chart shows Hard Coal -- Final Consumption by Country.
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure. Coal is composed primarily of carbon, along with variable quantities of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
coal has been used as an energy resource, primarily burned for the production of electricity and heat, and is also used for industrial purposes, such as refining metals. Coal is the largest source of energy for the generation of electricity worldwide, as well as one of the largest worldwide anthropogenic sources of carbon dioxide releases.
The extraction of coal, its use in energy production and its byproducts are all associated with environmental and health effects including climate change.Coal is extracted from the ground by coal mining.
Coal is one of the backstop resources that could limit escalation of oil prices and mitigate the effects of transportation energy shortage that will occur under peak oil. This is contingent on liquefaction production capacity becoming large enough to satiate the very large and growing demand for petroleum.
The energy density of coal, i.e. its heating value, is roughly 24 megajoules per kilogram. For a coal power plant with a 40% efficiency, it takes an estimated 325 kg of coal to power a 100 W lightbulb for one year.
9 years ago