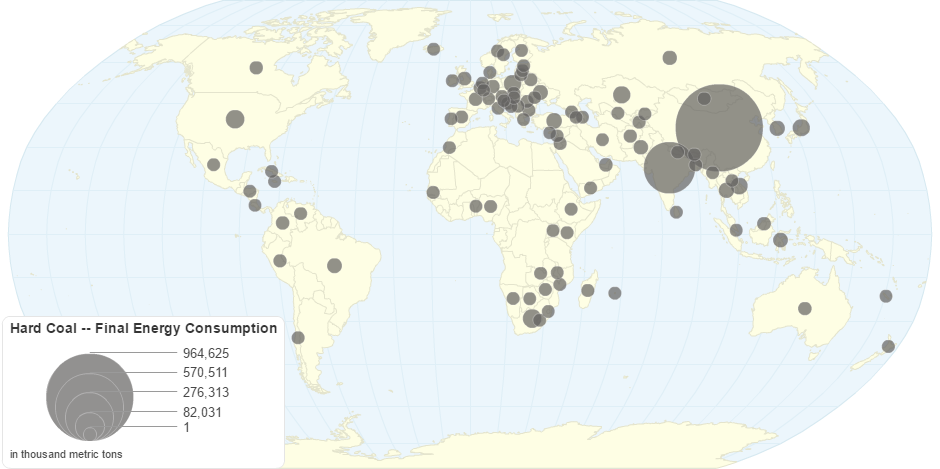
This chart shows Hard Coal -- Final Energy Consumption by Country.
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure. Coal is composed primarily of carbon, along with variable quantities of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
A fossil fuel, coal forms when dead plant matter is converted into peat, which in turn is converted into lignite, then sub-bituminous coal, after that bituminous coal, and lastly anthracite. This involves biological and geological processes that take place over time.
Coal has been used as an energy resource, primarily burned for the production of electricity and heat, and is also used for industrial purposes, such as refining metals. Coal is the largest source of energy for the generation of electricity worldwide, as well as one of the largest worldwide anthropogenic sources of carbon dioxide releases.
Coal is primarily used as a solid fuel to produce electricity and heat through combustion. World coal consumption was about 7.25 billion tonnes. and is expected to increase 48% to 9.05 billion tonnes by 2030.Efforts around the world to reduce the use of coal has led some regions to switch to natural gas.
Coke is a solid carbonaceous residue derived from low-ash, low-sulfur bituminous coal , from which the volatile constituents are driven off by baking in an oven without oxygen at temperatures as high as 1,000 °C , so the fixed carbon and residual ash are fused together. Metallurgical coke is used as a fuel and as a reducing agent in smelting iron ore in a blast furnace.The result is pig iron, and is too rich in dissolved carbon, so it must be treated further to make steel.
9 years ago