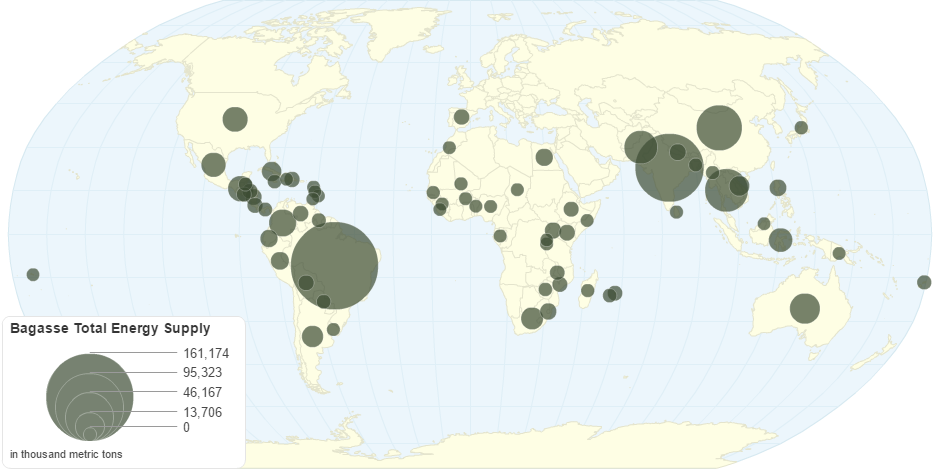
This chart shows Bagasse - Total energy supply by Country.
Bagasse is the fibrous matter that remains after sugarcane or sorghum stalks are crushed to extract their juice. It is dry pulpy residue left after the extraction of juice from sugar cane.Bagasse is utilized as a biofuel and in the manufacture of pulp and building materials.
'Agave bagasse" is a similar material that consists of the tissue of the blue agave after extraction of the sap.Bagasse can also be very useful to generate electricity. Dry bagasse is burnt in burners to produce steam, this steam is further used to rotate turbines hense producing electricity.
Bagasse is often used as a primary fuel source for sugar mills; when burned in quantity, it produces sufficient heat energy to supply all the needs of a typical sugar mill, with energy to spare. To this end, a secondary use for this waste product is in cogeneration, the use of a fuel source to provide both heat energy, used in the mill, and electricity, which is typically sold on to the consumer electricity grid.
Bagasse is commonly used as a substitute for wood in many tropical and subtropical countries for the production of pulp, paper and board, such as India, China, Colombia, Iran, Thailand and Argentina. It produces pulp with physical properties that are well suited for generic printing and writing papers as well as tissue products but it is also widely used for boxes and newspaper production.
Workplace exposure to dusts from the processing of bagasse can cause the chronic lung condition pulmonary fibrosis, more specifically referred to as bagassosis.
9 years ago