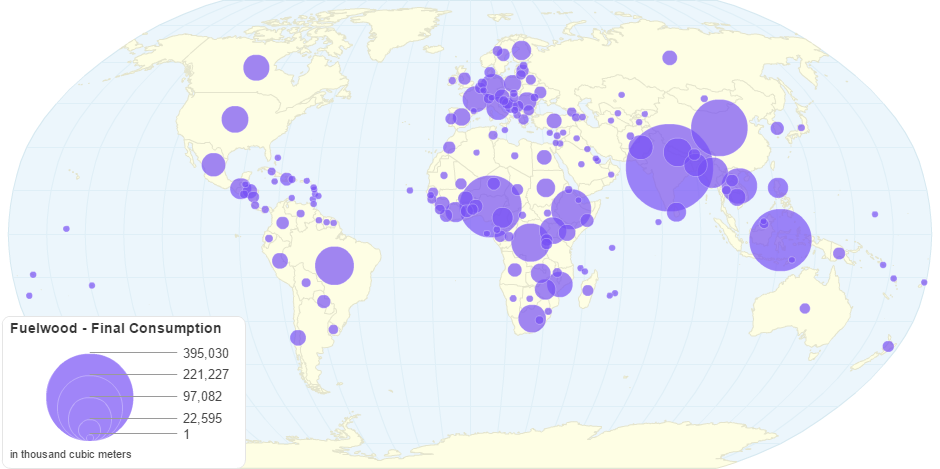
This chart shows Fuelwood Final Consumption by Country.
Wood fuel is a fuel, such as firewood, charcoal, chips, sheets, pellets, and sawdust. The particular form used depends upon factors such as source, quantity, quality and application. In many areas, wood is the most easily available form of fuel, requiring no tools in the case of picking up dead wood, or few tools, although as in any industry, specialized tools, such as skidders and hydraulic wood splitters, have been developed to mechanize production.
The discovery of how to make fire for the purpose of burning wood is regarded as one of humanity's most important advances. The use of wood as a fuel source for heating is much older than civilization and is assumed to have been used by Neanderthals. Today, burning of wood is the largest use of energy derived from a solid fuel biomass.
Wood fuel can be used for cooking and heating, and occasionally for fueling steam engines and steam turbines that generate electricity. Wood may be used indoors in a furnace, stove, or fireplace, or outdoors in a furnace, campfire, or bonfire.
Use of wood heat declined in popularity with the growing availability of other, less labor-intensive fuels.Wood heat was gradually replaced by coal and later by fuel oil, natural gas and propane heating except in rural areas with available forests.
Much wood fuel comes from native forests around the world. Plantation wood is rarely used for firewood, as it is more valuable as timber or wood pulp, however, some wood fuel is gathered from trees planted amongst crops, also known as agroforestry. The collection or harvesting of this wood can have serious environmental implications for the collection area. The concerns are often specific to the particular area, but can include all the problems that regular logging create.
9 years ago