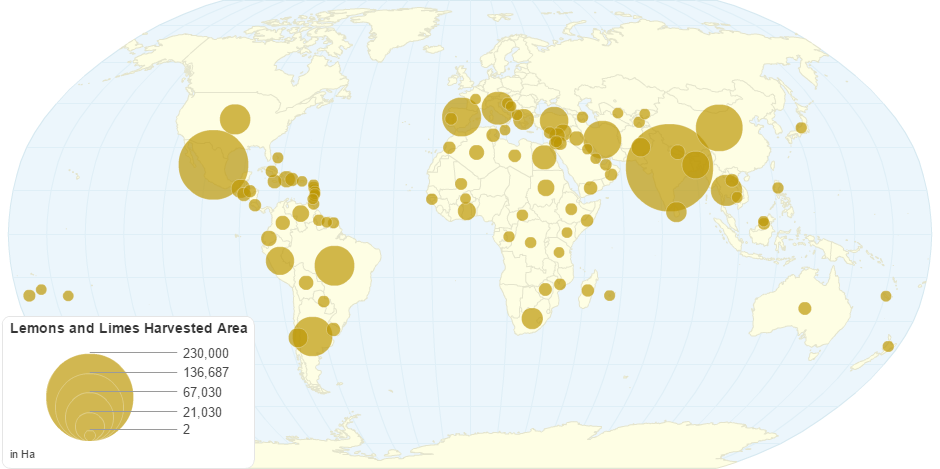
This chart shows Lemons and Limes Harvested Area by Country.
The lemon, Citrus limon Osbeck is a species of small evergreen tree in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia. The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culinary and non-culinary purposes throughout the world, primarily for its juice, which has both culinary and cleaning uses.The pulp and rind are also used in cooking and baking.
The juice of the lemon is about 5% to 6% citric acid, which gives a sour taste. The distinctive sour taste of lemon juice makes it a key ingredient in drinks and foods such as lemonade and lemon meringue pie.
Lemons are a rich source of vitamin C, providing 64% of the Daily Value in a 100 g serving. Other essential nutrients, however, have insignificant content .Lemons contain numerous phytochemicals, including polyphenols, terpenes, and tannins.As with other citrus fruits, they have significant concentrations of citric acid.
Lemon juice and rind are used to make marmalade, lemon curd and lemon liqueur. Lemon slices and lemon rind are used as a garnish for food and drinks. Lemon zest, the grated outer rind of the fruit, is used to add flavor to baked goods, puddings, rice, and other dishes.
A lime is a hybrid citrus fruit, which is typically round, lime green, 3–6 centimetres in diameter, and containing acidic juice vesicles.There are several species of citrus trees whose fruits are called limes, including the Key lime , Persian lime, kaffir lime, and desert lime.
Limes are an excellent source of vitamin C, and are often used to accent the flavours of foods and beverages. They are grown year-round.Plants with fruit called "limes" have diverse genetic origins; limes do not form a monophyletic group.
Raw limes are 88% water, 10% carbohydrates and less than 1% each of fat and protein. Only vitamin C content at 35% of the Daily Value (DV) per 100 g serving is significant for nutrition, with other nutrients present in low DV amounts.
9 years ago