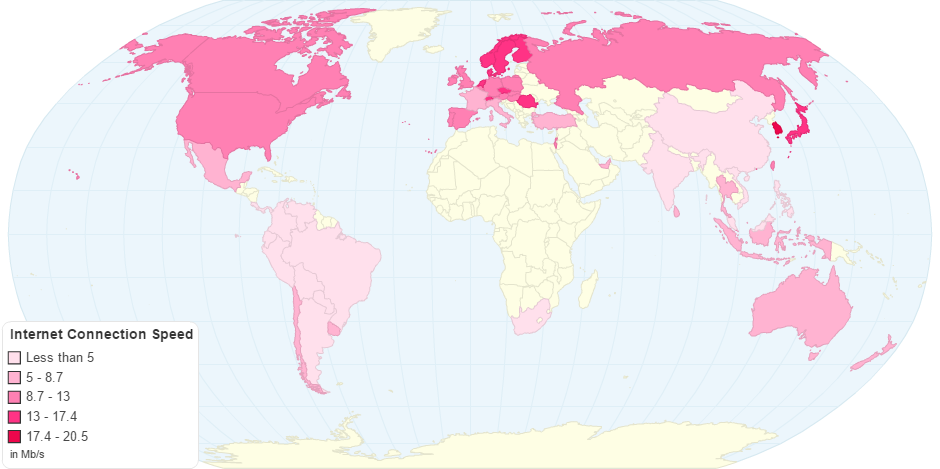
This chart shows Internet Connection Speed by Country.
The Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that use the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to link billions of devices worldwide. It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies.
The Internet carries an extensive range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web, electronic mail, voice over IP telephony, and peer-to-peer networks for file sharing.
Internet access is the process that enables individuals and organisations to connect to the Internet using computer terminals, computers, mobile devices, sometimes via computer networks. Once connected to the Internet, users can access Internet services, such as email and the World Wide Web. Internet service providers offer Internet access through various technologies that offer a wide range of data signaling rates.
Consumer use of the Internet first became popular through dial-up Internet access in the 1990s. By the first decade of the 21st century, many consumers in developed nations used faster, broadband Internet access technologies. By 2014 this was almost ubiquitous worldwide, with a global average connection speed exceeding 4 Mbit/s.
9 years ago